Publication
A Mathematical Description of the Bone Marrow Dynamics of CAR T-Cell Therapy in B-cell Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
A. Martínez-Rubio, S. Chulián, C. Blázquez Goñi, A. Pérez Martínez, M. Ramírez Orellana, A. Navarro-Zapata, C. Ferreras, V.M. Pérez-García, M. Rosa
International J. of Molecular Sciences 22, 6371 (2021)
MOLAB authors
Abstract
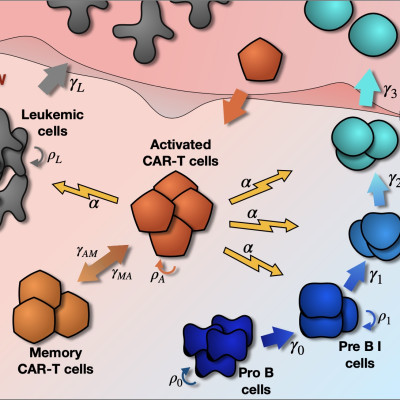
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has demonstrated high rates of response in recurrent B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in children and young adults. Despite this success, a fraction of patients experience relapse after treatment. Relapse is often preceded by recovery of healthy B cells, which suggests loss or dysfunction of CAR T cells in bone marrow. This site is harder to access, and thus is not monitored as frequently as peripheral blood. Understanding the interplay between B cells, leukemic cells and CAR T cells in bone marrow is paramount in ascertaining the causes of lack of response. In this paper, we put forward a mathematical model representing the interaction between constantly renewing B cells, CAR T cells and leukemic cells in the bone marrow. Our model accounts for the maturation dynamics of B cells and incorporates effector and memory CAR T cells. The model provides a plausible description of the dynamics of the various cellular compartments in bone marrow after CAR T infusion. After exploration of the parameter space, we found that the dynamics of CAR T product and disease were independent of the dose injected, initial B-cell load and tumor burden. We also show theoretically the importance of CAR T product attributes in determining therapy outcome, and have studied a variety of possible response scenarios, including second dosage schemes. We conclude by setting out ideas for the refinement of the model.